Cloud Delivery Models
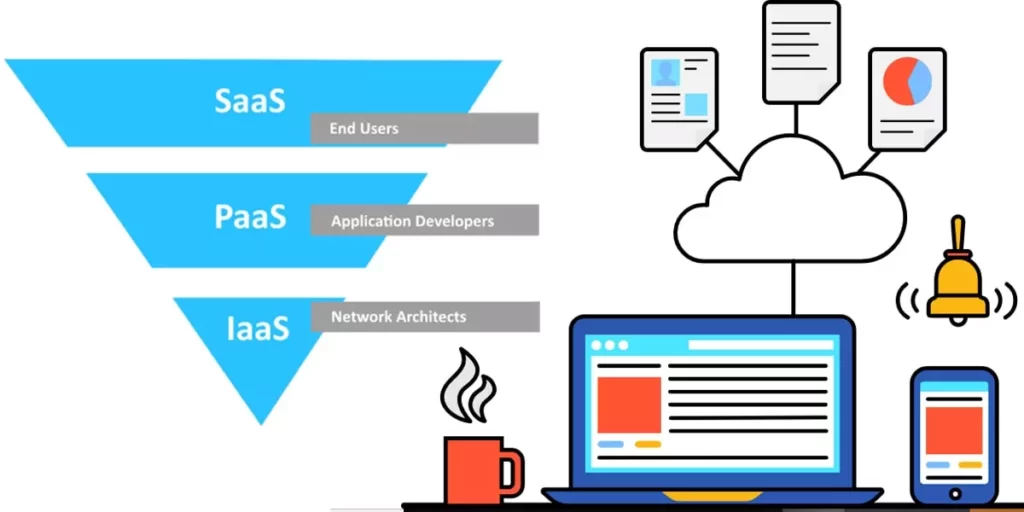
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications deliver software that users access through a browser over the Internet. Vendors manage hardware, databases, security, and infrastructure, but users can usually configure software to suit their needs. For example, customer relationship management for sales, service, marketing, HR software for HR.
SaaS: Software-as-a-service (SaaS)
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications deliver software that users access through a browser over the Internet. Vendors manage hardware, databases, security, and infrastructure, but users can usually configure software to suit their needs. For example, customer relationship management for sales, service, marketing, HR software for HR.
PaaS: Platform-as-a-service (PaaS)
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) cloud solutions provide developers with the software and operating systems they need to build cloud-based applications. Whether it’s a mobile app for better inventory tracking or a social media platform for consumers. Enterprises are starting to use PaaS cloud systems for network security because they can easily customize them to their specific security requirements.
Multi Cloud
Certain companies want to distribute their internal computer processing and storage requirements across multiple cloud platforms and applications from different vendors, often based on their needs.
For example, it is common to choose different cloud providers for different features such as ERP, security, and marketing technology. An all-in-one business management platform that supports a large number of features is the best option for many companies, but it may still require complementary solutions to support other areas of the business.
Enterprises may also extend the use of public clouds to their computing resources to avoid lock-ins and leverage them in negotiations.
Private cloud
A private cloud is a cloud computing model in which services are provided through a private infrastructure to use a single business, usually managed by the same business. Businesses are choosing private cloud to enjoy the benefits of cloud services through vendors without taking the cost of building and maintaining the cloud infrastructure itself.
Hybrid cloud
Many companies are opting for a hybrid cloud model that combines public cloud services with a single business-only private cloud deployment. This is especially true for organizations that collect sensitive data or do business in highly regulated industries such as insurance where data privacy is essential.
The hybrid approach is attractive because it provides customers with the level of control they need without disrupting innovation or scale as they deploy new services.
Serverless
Serverless computing is a type of cloud computing that enables enterprises to access their IT infrastructure on demand without the need for capital investment or management of the infrastructure itself.
The difference between general cloud computing and serverless is based on how resources are allocated. Serverless is a subset of PaaS used by enterprises that require a lot of processing power, but bursts are short. Compiling software code is one example.
The serverless model is attracting attention among large and small businesses that want to build new applications quickly but lack the time, resources, and budget to process their infrastructure. This will enable growing companies to leverage better computing power at a reasonable cost, allowing large organizations to deploy new digital services without increasing the burden on their already growing IT teams.
In fact, 25% of developers will be using serverless computing by the end of 2021, global research firm Forrester predicts.
Join our news Letter
- Revolutionizing Parking Management A Real-Time Example
- The Importance of Regular Application Maintenance
- Logistics Software Solutions and Software Development
- Software Development Services for SMEs
- How Does IoT Aid Businesses in a Variety of Industries
- But what exactly is IoT – What does it mean for manufacturers – How can you use IoT to improve your business
- How to outsource custom software development Services
- 5 Reasons Why You Need To Outsource Software Development
- Why You Need A Cloud Strategy
- The Cloud Is Changing Everything, Here’s How To Make It Work For Your Business
Do you require Mobile App Development Services?
Looking for experienced mobile app developers to create a web app from the ground up, or do you want us to get started on an existing project? Get your no-obligation expert consultation today!

